Order has different stages. It is first entered into system then it gets schedule. After scheduling it gets picked/packed and shipped. After shipping it gets invoiced and then finally closed. There are multiple system and entities involved in complete life cycle of Order.
Oracle has come up with Orchestration which is a set of activities performed on any single Order to complete its Life cycle. These activities can be performed as a single step across large number of systems. It comes up with a workflow automation tool in Oracle Cloud define schedules for workflow executions repeatedly or in the future.
Snapshot of Orchestration
Orchestration Groups
All fulfillment lines that belong to an orchestration group are assigned the same Orchestration Process. Types of Orchestration groups:
- Shipment Set : A set of order lines that Order Management ships together as one group. All these order lines, ship and arrive on the same date, although they might be spread across more than one package, depending on packing requirements.
- Model/Kit : A configured item that includes one or more configure options.
- Standard : Group of Standard items(not configured) or finished items.
Orchestration Process Components.
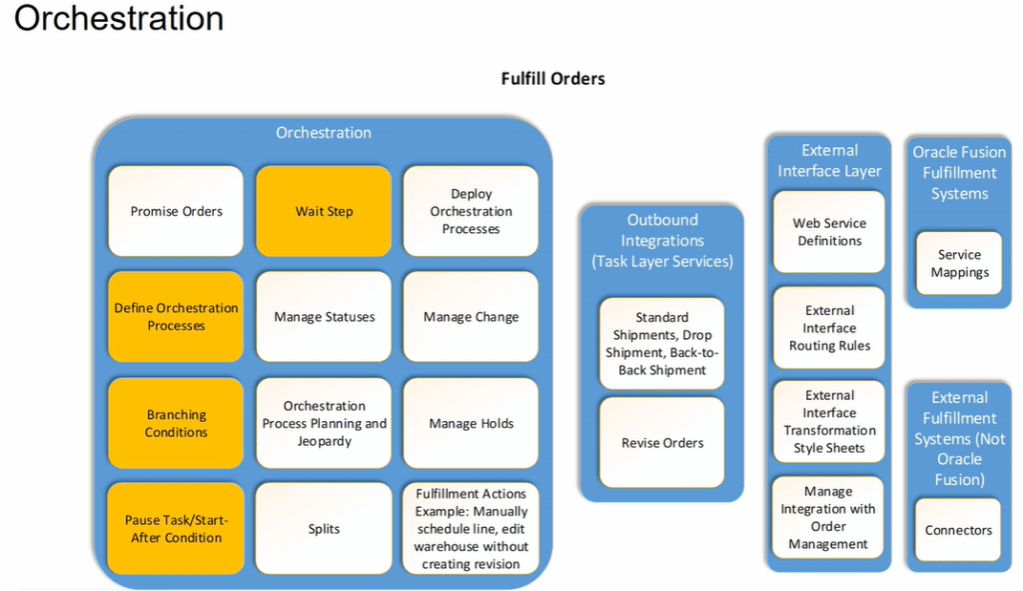
Fulfillment of any Order happens using Orchestration process which has 4 components to it.
- Within Orchestration Process -> Task like Shipment, Invoices etc. which takes care of activity within fusion.
- Outbound Integrations/Task Layer Services -> Order Management different tasks like Shipment, Invoices etc. connects with fulfillment system using Outbound Integrations.
- External Interface Layer -> It uses different technique i.e. web services, Routing Rules, TSS etc. to communicate specific task from OM system to Fulfillment systems.
- Orchestration Fulfillment Systems-> It could be either Inventory system, Shipping or Invoicing system within Oracle cloud or could be External fulfillment system.
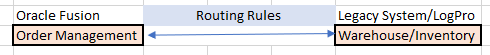
Example: We could be using Oracle fusion for Order management and Legacy system of Warehouse. We need to setup communication using External Interface Layer(Routing Rules) .
Orchestration Processes Life Cycle
- Create/Copy Orchestration Process
- Validate Process
- Release Process
- Deploy Process
Default Orchestration Process Provided By Oracle
- DOO_BillOnlyGenericProcess –> Used for Invoice for items like Extended warranty which are not physical items. It can only be billed but cannot be shipped.
- DOO_OrderFulfillmentGenericProcess
- DOO_SubmitSalesOrderProcess
- ReturnOrderGenericProcess –> It is used for Return. It follows cycle of Return -> Invoice
- ShipOrderGenericProcess –> It follow cycle of Schedule -> Reserve -> Ship -> Invoice
Navigation: Go To setup and Maintenance -> Order Management -> Select task “Manage Orchestration Process Definition.
List of Available Orchestration process will appear. Select DOO_OrderFulfillmentGenericProcess and click on Edit. Below screen appears.
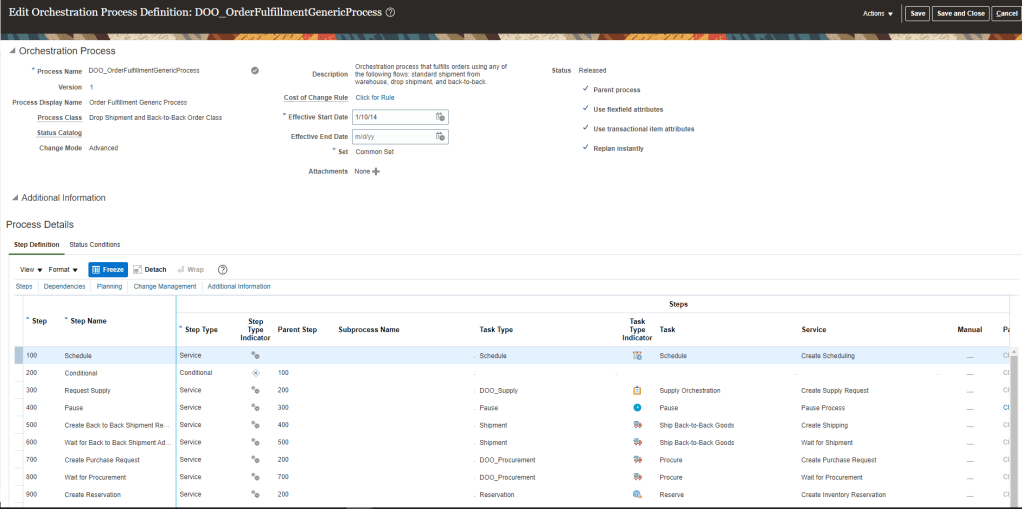
Oracle Business Rules(OBR) in Orchestration Process
Attributes in Process definition of Orchestration, uses OBR to make runtime decisions for process behavior:
- Cost of Change: It is not measured in monetary terms rather its measured in resources getting utilized when any changes are to be made in an order. It gives ranking in difficulty of making changes and whether the change should be allowed.
- Compensation Pattern: If changes are allowed in order then whether all steps needs to be executed or only few steps needs to be executed and already executed steps need not run.
- Lead Time Expression : Time taken to run or rerun the task of orchestration process.
- Line Selection Criteria : If change is to be allowed in Order, than this criteria helps to filter out steps which do not affect re-planning.
- Branching Condition : Set criteria to call different branches.
- Pause Rule : To wait until a task gets executed.
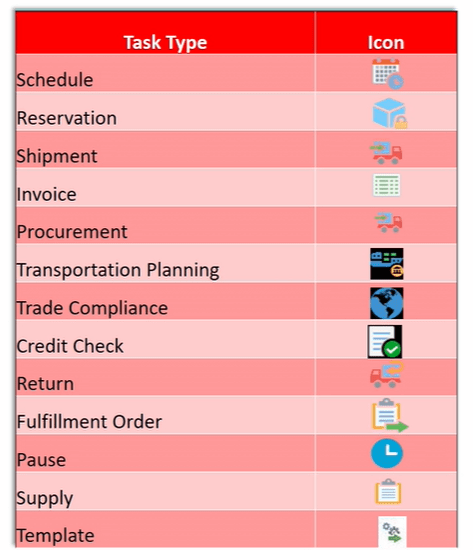
Tasks within Orchestration Process
Below are the different task we have in our Orchestration Process.
Status in Orchestration Process
Statuses play key role in Order Management to determine the life cycle of Order. Any order goes through series of steps and Status helps in identifying the current status of order. Status defined in Orchestration Process will reflect in Order Management.
Please refer to link to get complete picture of Status, How to create new setups as well as custom defined setup done in Orchestration process Definition
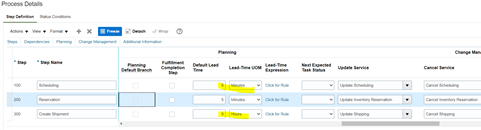
Planning Parameters to an Orchestration Process Definition
Planning Parameters decides how much time each task within Orchestration Process will take , which will give estimate of sum total time taken by complete orchestration process.
- Navigation: Go to Others -> Setup and Maintenance -> Order Management -> Enter Rules “Manage Orchestration Process Definition”
- Edit Existing Orchestration Process
- Go Planning tab, under Step Definition of Process Details
- Enter Default Lead time and lead Time UOM.
- Lead time determines max time taken by each steps under normal circumstances.
Making changes to Orchestration Process
Suppose we need to make any change to Task like “Pause Rule”
- Go to Others -> Setup and Maintenance -> Order Management -> Enter Rule “Manage Orchestration Process Definition”.
- Create a new orchestration process definition or choose existing definition
- Go to Pause step and click on “Click for Rule”
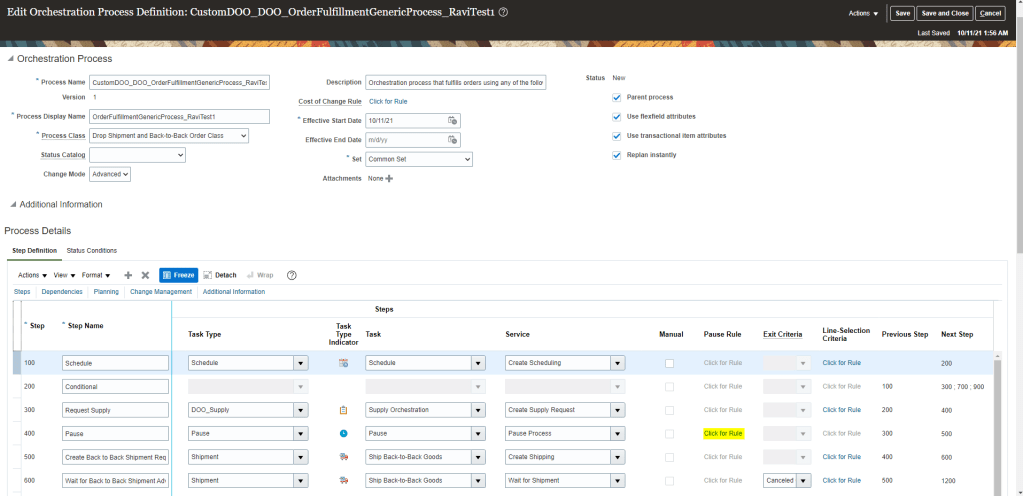
- Below Rule Set screen appears. Click on Green Plus Button to create new Rule.
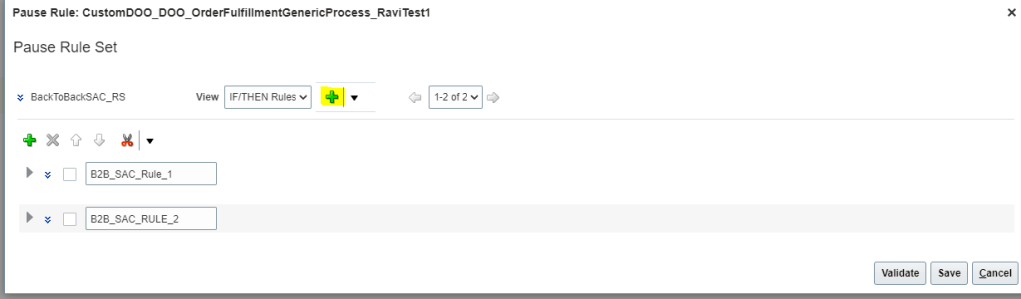
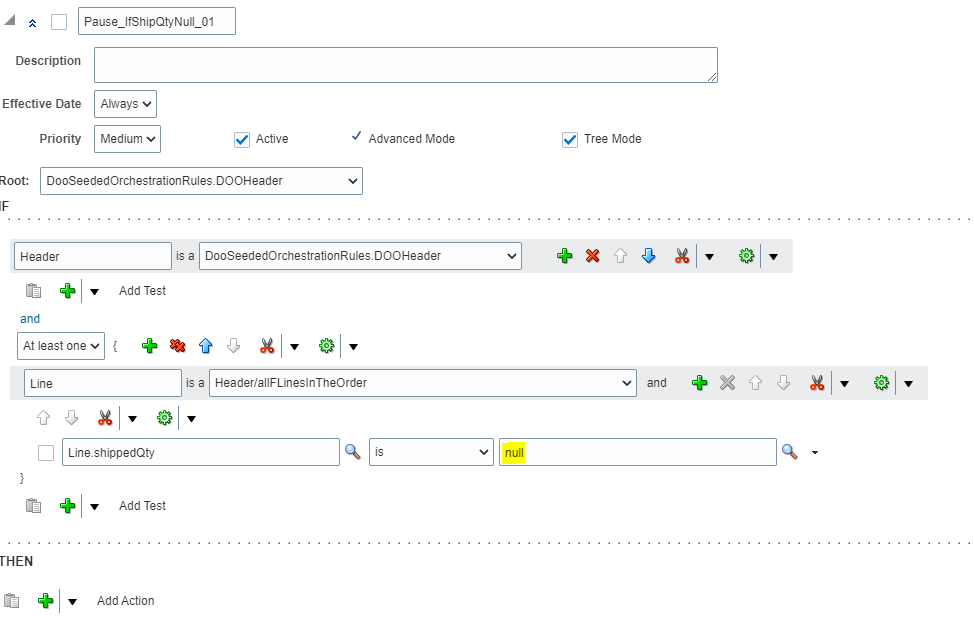
- Give Name of the Rule = “Pause_IfShipQtyNull_01” . Check Active, Advanced and Tree Mod
- Open the Root list and then select “DooSeededOrchestrationRules.DOOHeader” list item.
- Underneath the IF label, in the left field that contains DooSeededOrchestrationRules.DOOHeader, substitute the current text with Header.
- Below Header -> Click on Search Button and from Drop down select “Delete Test” to the delete additional line.
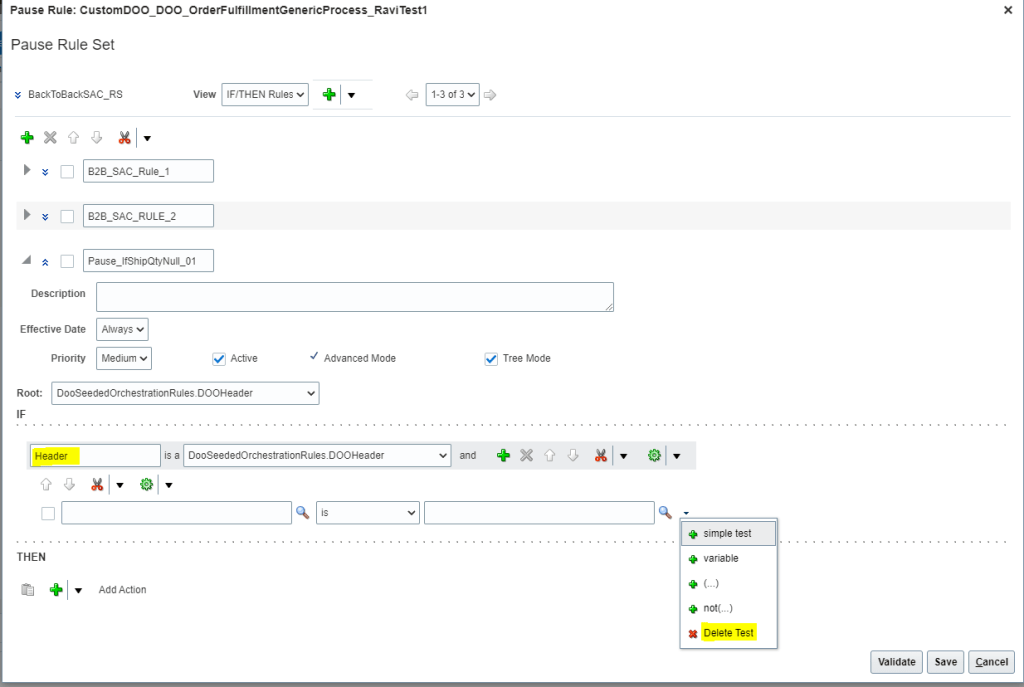
- To the right of DooSeededOrchestrationRules.DOOHeader, click the Add Pattern icon
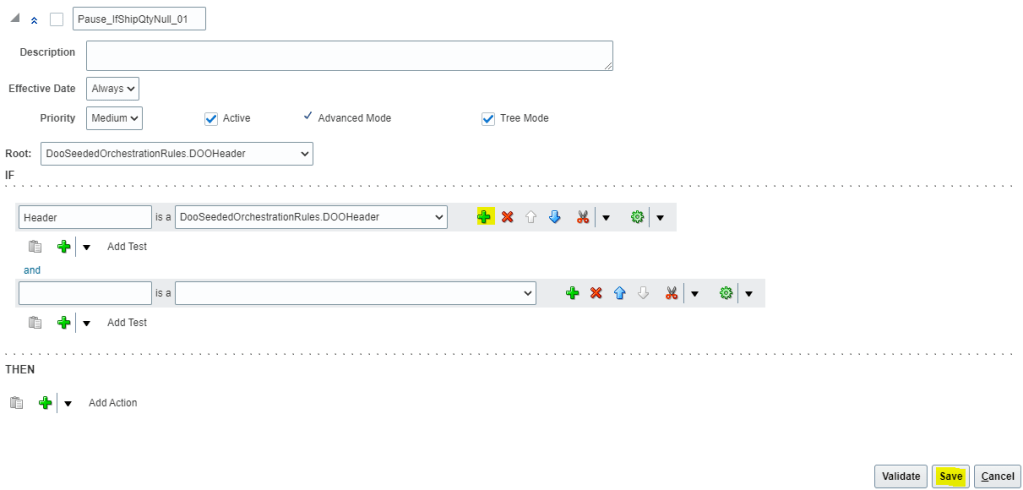
- Below Header section in the and section, Leave first field immediately to the left of “Is A”, blank . In the list to the right of “Is A”, select Header/allFLinesInTheOrder. The left portion will get defaulted to value “Header/allFLinesInTheOrder”.
- To the right of the field that you set to Header/allFLinesInTheOrder, click the down arrow next to the Surround Pattern With Parentheses icon and then select Surround
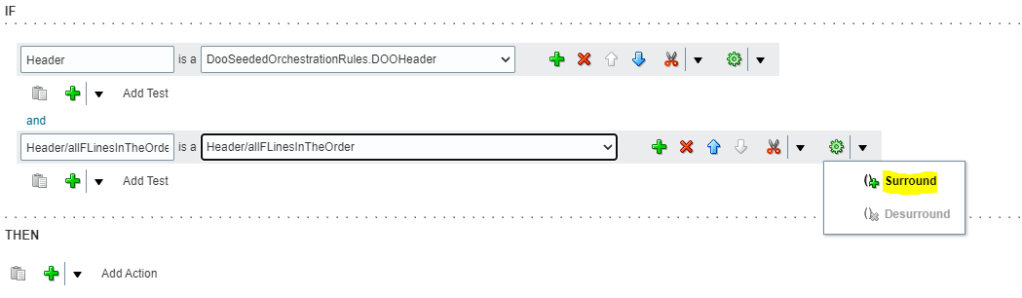
- Change the Left section to meaningful name “Line”
- Below “Header” and after “and”, change the value from “Each” to “At least one.”
- Directly below the field that contains “Line,” click the arrow next to Add Test and then select Simple Test.
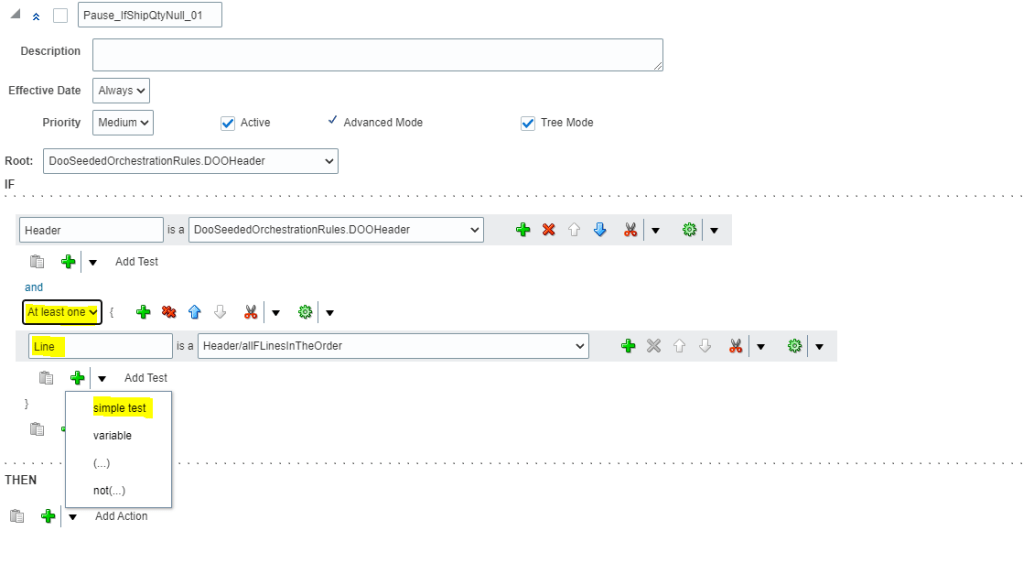
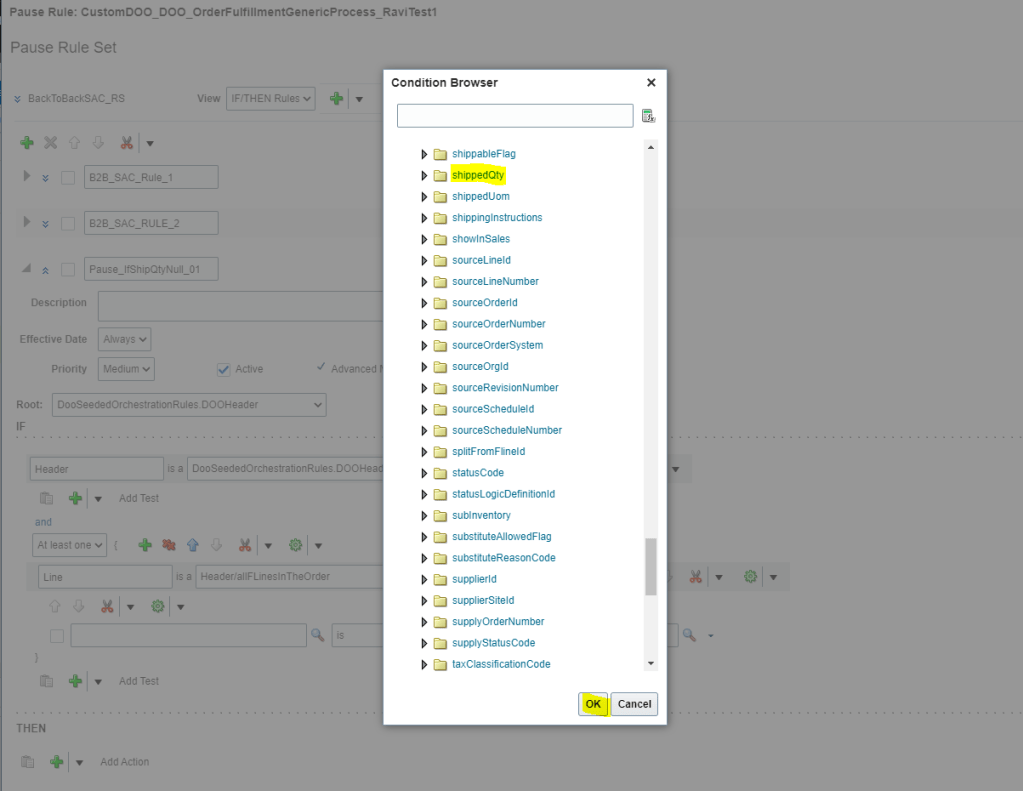
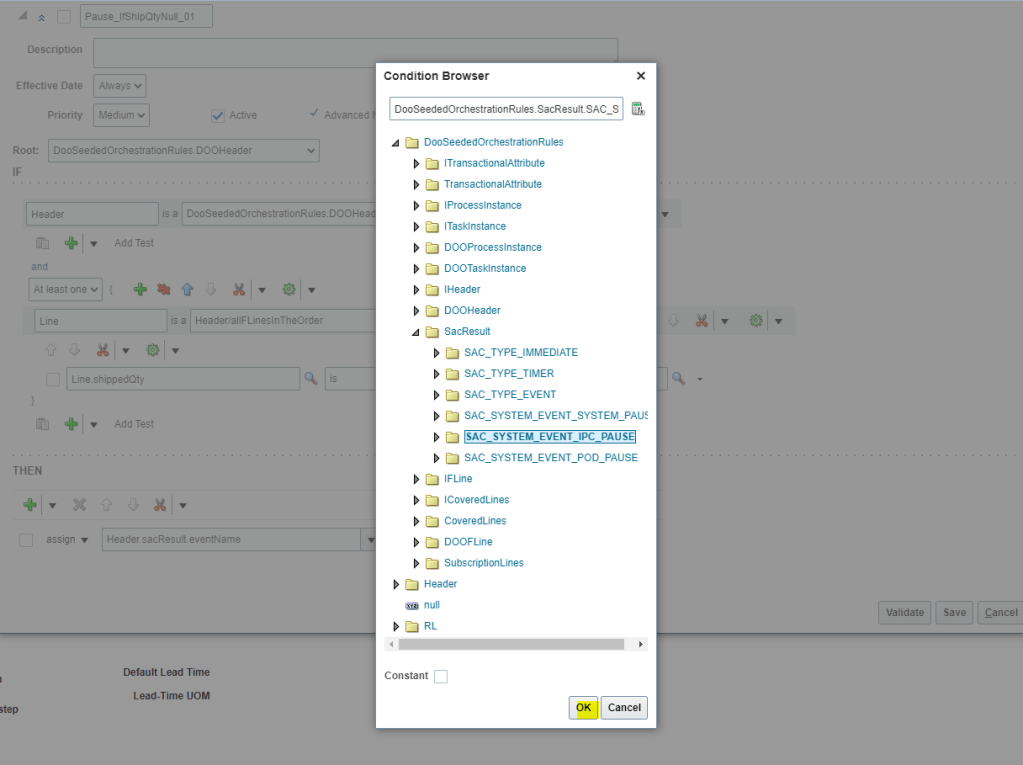
- In the Condition Browser on Left Side, expand Line, and then select “shippedQty” and click OK.
- In the Right side In the Condition Browser, click null.
- In “THEN” region, click the Add Action list, and select assign.
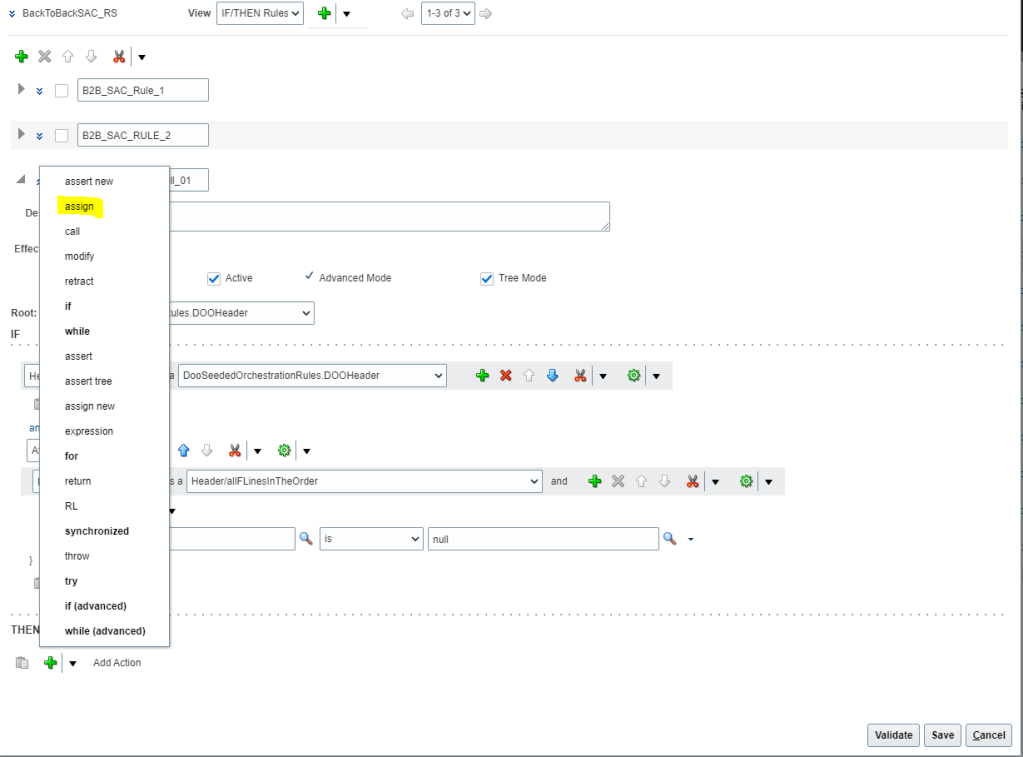
- In the Select a Target list, select “Header.sacResult.eventName” and on left side In the Condition Browser, expand DooSeededOrchestrationRules and then SacResult. Select “SAC_SYSTEM_EVENT_IPC_PAUSE”.
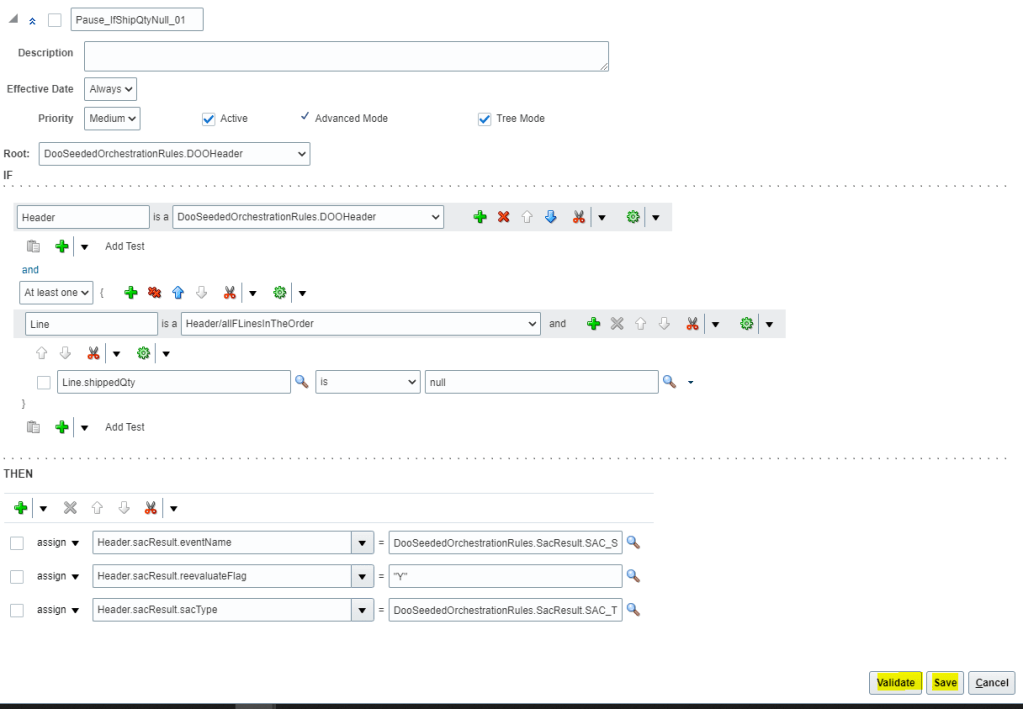
- In the Select a Target list, select Header.sacResult.reevaluateFlag and on right side Click Expression Value. In the Condition Browser, enter “Y”.
- In the Select a Target list, select Header.sacResult.sacType and on right side Condition Browser, expand DooSeededOrchestrationRules, expand SacResult, and then click SAC_TYPE_EVENT
- In the Pause Rule: CustomDOO_OUStandardOrdersProcessXX window, click Validate
Steps to Deploy Orchestration Process Definition
- Refer to Steps mentioned at Link to get complete understanding/steps to be performed for Deployment of Orchestration process definition.
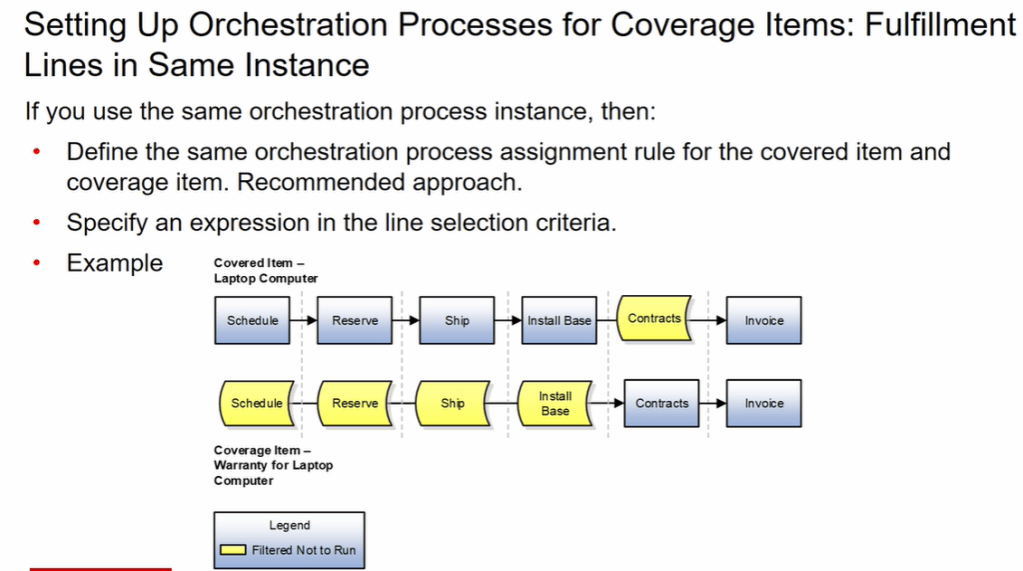
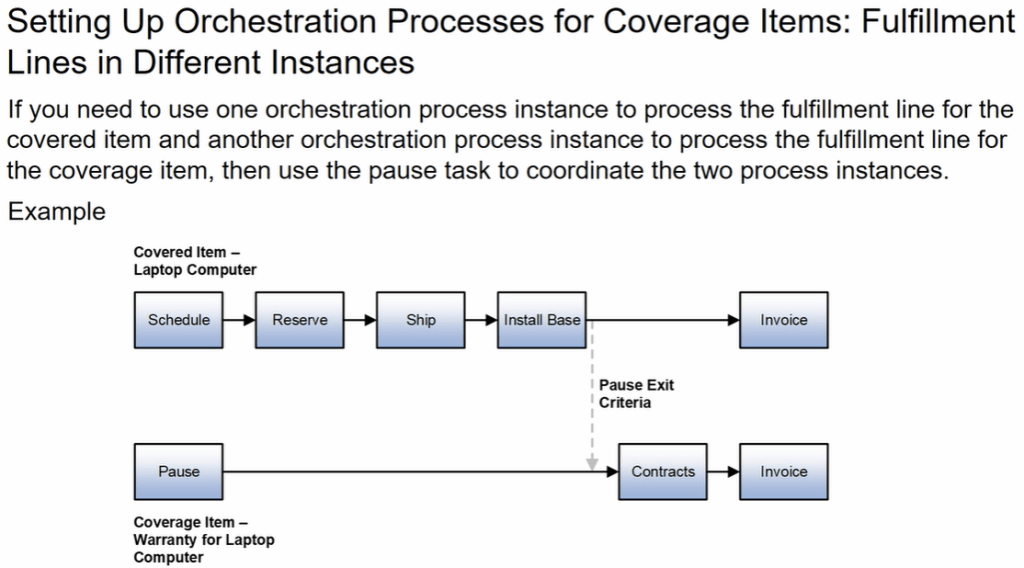
Orchestration for Coverage Items